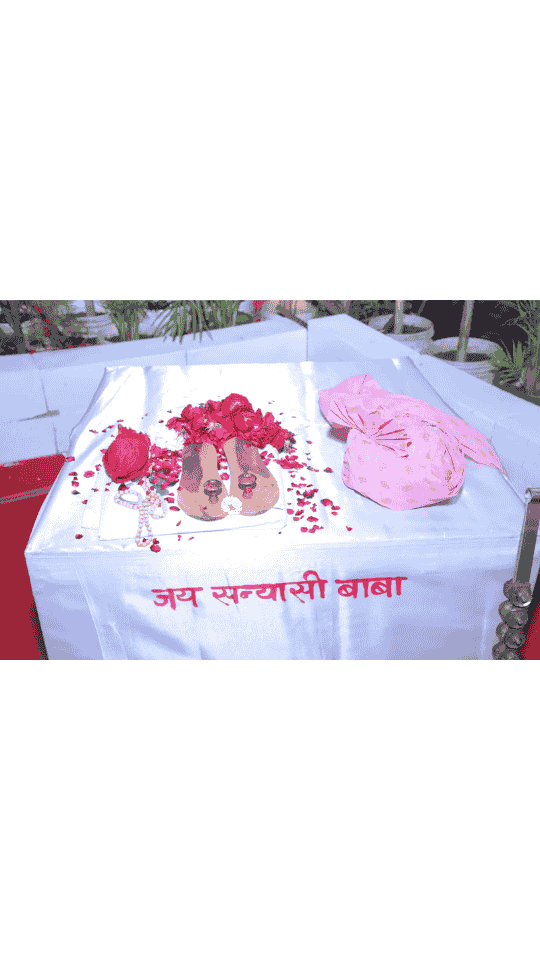

सन्यासी बाबा

कैंसर हॉस्पिटल

संत सम्मेलन
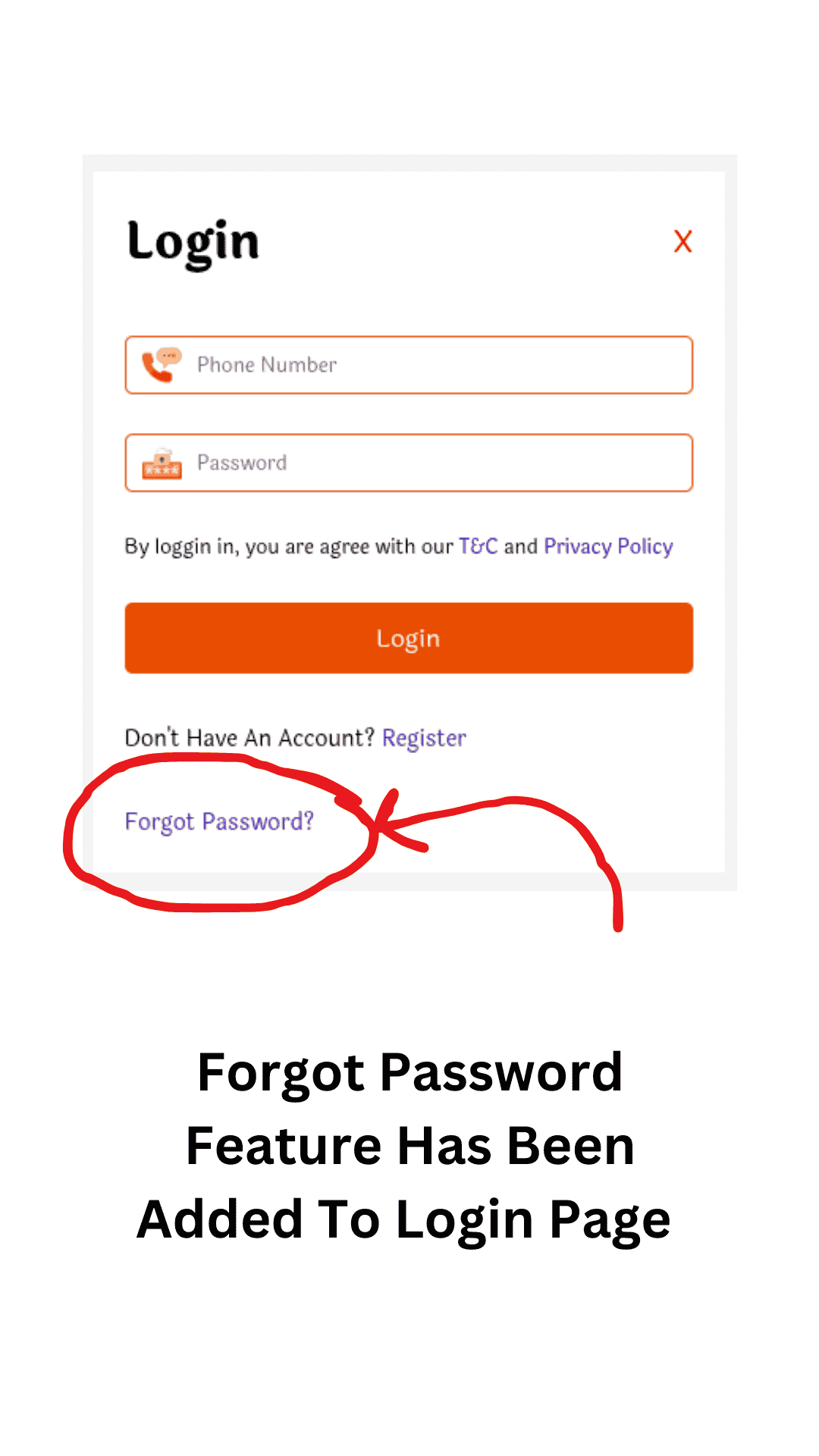
Forgot Password

Mahakumbh
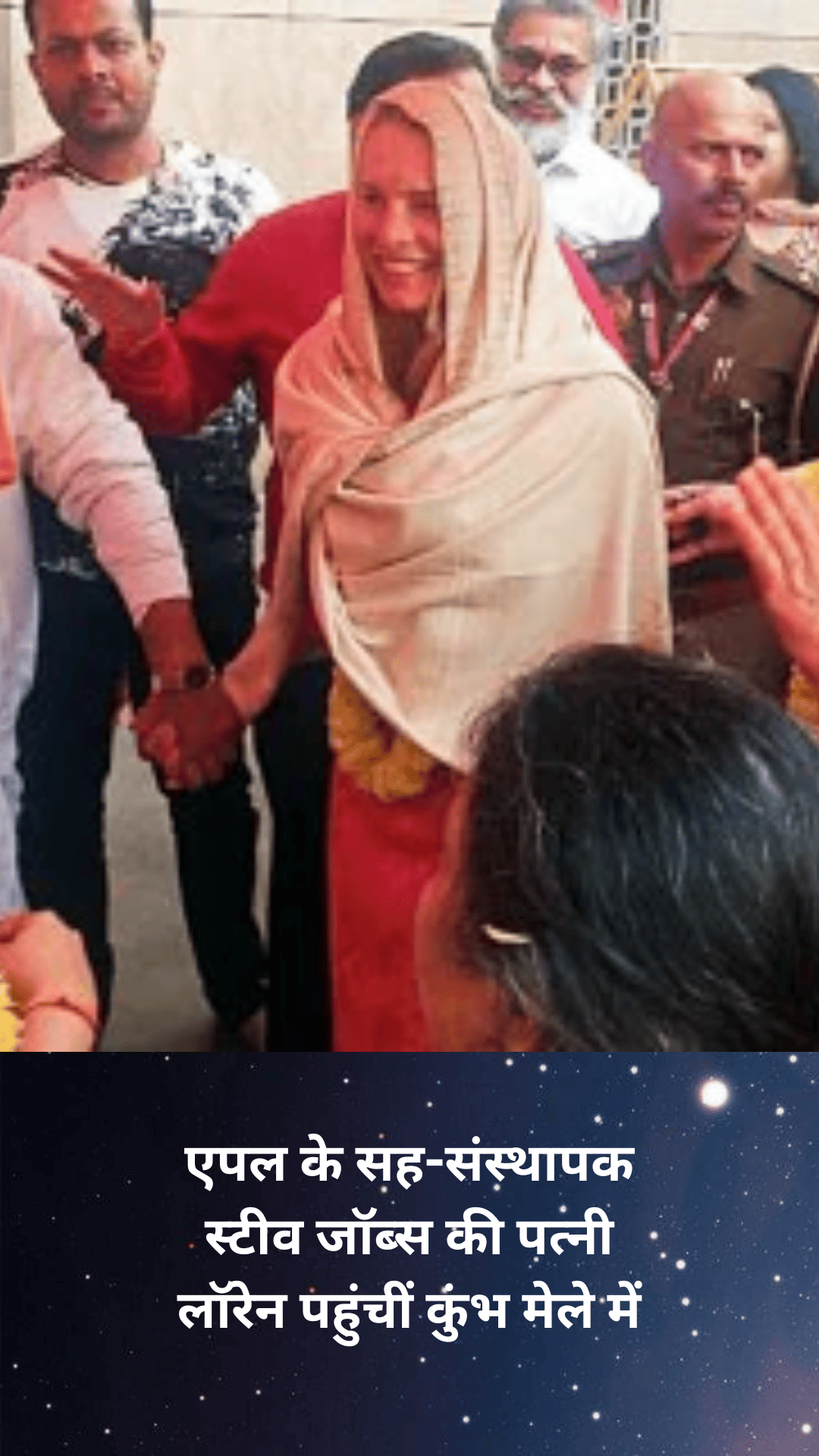

लॉरेन पावेल

रामलला दर्शन

साधू जी सीताराम

ffd er re

sd rt wer t
sd g rt wer

exapj o d
this is first
हिंदू धर्म में कर्म एक केंद्रीय और महत्वपूर्ण अवधारणा है। कर्म शब्द संस्कृत के कृ से लिया गया है जिसका अर्थ है करना या कार्य। यह सिद्धांत कहता है कि हर व्यक्ति के कार्यों का एक परिणाम होता है जो उसके वर्तमान और भविष्य के जीवन को प्रभावित करता है। सनातन धर्म में कर्म को जीवन का नियम माना जाता है जो नैतिकता और जिम्मेदारी पर आधारित है।
कर्म तीन प्रकार के होते हैं: संचित कर्म (पिछले जन्मों से जमा), प्रारब्ध कर्म (इस जन्म का हिस्सा) और क्रियमाण कर्म (वर्तमान में किए गए कार्य)। उदाहरण के लिए भगवद् गीता में श्रीकृष्ण अर्जुन को सिखाते हैं कि कर्म फल की चिंता किए बिना निस्वार्थ भाव से करना चाहिए। यह न केवल व्यक्तिगत विकास के लिए है बल्कि समाज के लिए भी।
कारण और प्रभाव: हर कार्य का परिणाम होता है।
पुनर्जन्म: कर्म पिछले और अगले जन्म को जोड़ता है।
स्वतंत्रता: व्यक्ति अपने कर्म से भाग्य बनाता है।
निस्वार्थता: फल की इच्छा के बिना कर्म करना।
कर्म जीवन को संतुलित करता है। यह सिखाता है कि अच्छे कार्य सुख लाते हैं और बुरे कार्य दुख। यह नियम हर किसी पर लागू होता है चाहे वह राजा हो या सामान्य व्यक्ति।
In Hinduism, Karma is a central and vital concept. Derived from the Sanskrit root kṛ, meaning to do or act, Karma refers to the principle that every action has a consequence, shaping one’s present and future lives. In Sanatana Dharma, Karma is seen as a law of life rooted in morality and responsibility.
Karma is categorized into three types: Sanchita Karma (accumulated from past lives), Prarabdha Karma (portion active in this life), and Kriyamana Karma (actions performed now). For instance, in the Bhagavad Gita, Lord Krishna teaches Arjuna to perform actions selflessly, without attachment to outcomes, benefiting both the individual and society.
Cause and Effect: Every action leads to a result.
Rebirth: Karma connects past and future lives.
Freedom: Individuals shape their destiny through actions.
Selflessness: Acting without desire for rewards.
Karma brings balance to life. It teaches that good actions lead to happiness and bad actions to suffering. This law applies to everyone, whether a king or a commoner.

2025-01-10

2025-03-27

2025-03-28

2025-02-07

2025-05-21

2025-02-07

2025-02-08

2025-02-08